Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Ikken; Yoshikawa, Shinji; Yamashita, Takuya; Shimomura, Kenta; Cibula, M.*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 422, p.113088_1 - 113088_24, 2024/06
Suyama, Kenya; Ueki, Taro; Gunji, Satoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Araki, Shohei; Fukuda, Kodai; Yamane, Yuichi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Kikuchi, Takeo; et al.
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/10
To remove and store safely the fuel debris generated by the severe accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011 is one of the most important and challenging topics for decommissioning of the damaged reactors in Fukushima. To validate the adopted method for the evaluation of criticality safety control of the fuel debris through comparison with the experimental data obtained by the criticality experiments, the Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) of Japan funds a research and development project which was entrusted to the Nuclear Safety Research Center (NSRC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) from 2014. In this project, JAEA has been conducting such activities as i) comprehensive computation of the criticality characteristics of the fuel debris and making database (criticality map of the fuel debris), ii) development of new continuous energy Monte Carlo code, iii) evaluation of criticality accident and iv) modification of the critical assembly STACY for the experiments for validation of criticality safety control methodology. After the last ICNC2019, the project has the substantial progress in the modification of STACY which will start officially operation from May 2024 and the development of the Monte Carlo Code "Solomon" suitable for the criticality calculation for materials having spatially random distribution complies with the power spectrum. We present the whole picture of this research and development project and status of each technical topics in the session.
Gunji, Satoshi; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Araki, Shohei; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
Since the compositions and properties of the fuel debris are uncertain, critical experiments are required to validate calculation codes and nuclear data used for the safety evaluation. For this purpose, JAEA has been modifying a critical assembly called "STACY". The first criticality of the new STACY is scheduled for spring 2024. This paper reports the consideration results of the core configurations of the new STACY at the first criticality. We prepared two sets of gird plates with different neutron moderation conditions (their intervals are 1.50 cm and 1.27 cm). However, there is a limitation on the number of available UO fuel rods. In addition, we would like to set the critical water heights for the first criticality at around 95 cm. This is to avoid the reactive effect of the aluminum alloy middle grid plates (Approx. 98 cm high). The core configurations for the first criticality satisfying these conditions were constructed by computational analysis. A square core configuration with the 1.50 cm grid plate that is close to the optimum moderation condition needs 261 fuel rods to reach criticality. As to the 1.27 cm grid plate, we considered two core configurations with 1.80 cm intervals by using a checkerboard arrangement. One of them has two regions core configuration with 1.27 and 1.80 cm intervals, and the other has only 1.80 cm intervals. They need 341 and 201 fuel rods for the criticality, respectively. This paper shows these three core configurations and their calculation models.
fuel rods. In addition, we would like to set the critical water heights for the first criticality at around 95 cm. This is to avoid the reactive effect of the aluminum alloy middle grid plates (Approx. 98 cm high). The core configurations for the first criticality satisfying these conditions were constructed by computational analysis. A square core configuration with the 1.50 cm grid plate that is close to the optimum moderation condition needs 261 fuel rods to reach criticality. As to the 1.27 cm grid plate, we considered two core configurations with 1.80 cm intervals by using a checkerboard arrangement. One of them has two regions core configuration with 1.27 and 1.80 cm intervals, and the other has only 1.80 cm intervals. They need 341 and 201 fuel rods for the criticality, respectively. This paper shows these three core configurations and their calculation models.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Arakaki, Yu; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/10
JAEA has been modifying a critical assembly called STACY from a solution system to a light-water moderated heterogeneous system to validate computation results of criticality characteristics of fuel debris generated in the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. To experimentally simulate the composition and characteristics of fuel debris, we will prepare several grid plates which make particular neutron moderation conditions and a number of rod-shaped concrete and stainless-steel materials. Experiments to evaluate fuel debris's criticality characteristics are scheduled using these devices and materials. This series of STACY experiments are planned to measure the reactivity of fuel debris-simulated samples, measure the critical mass of core configurations containing structural materials such as concrete and stainless steels, and the change in critical mass when their arrangement becomes non-uniform. Furthermore, two divided cores experiments are scheduled that statically simulate fuel debris falling, and also scheduled that subcriticality measurement experiments with partially different neutron moderation conditions. The experimental plans have been considered taking into account some experimental constraints. This paper shows the schedule of these experiments, as well as the computation results of the optimized core configurations and expected results for each experiment.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Fernex, F.*; Leclaire, N.*; Bardelay, A.*; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/10
Institut de radioprotection et de s ret
ret nucl
nucl aire (IRSN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have a long-standing partnership in the field of criticality safety. In this collaboration, IRSN and JAEA are planning a joint experiment using the new STACY critical assembly, modified by JAEA. In order to compare the codes (MVP3, MORET6, etc.) and nuclear data (JENDL and JEFF) used by both institutes in the planning of the STACY experiment, benchmark calculations of the Apparatus B and TCA, which are critical assemblies once owned by both institutes, benchmarks from the ICSBEP handbook and the computational model of the new STACY were performed. Including the new STACY calculation model, the calculations include several different neutron moderation conditions and critical water heights. There were slight systematic differences in the calculation results, which may have originated from the processing and/or format of the nuclear data libraries. However, it was found that the calculated results, including the new codes and the new nuclear data, are in good agreement with the experimental values. Therefore, there are no issues to use them for the design of experiments for the new STACY. Furthermore, the impact of the new TSL data included in JENDL-5 on the effective multiplication factor was investigated. Experimental validation for them will be completed by critical experiments of the new STACY by both institutes.
aire (IRSN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have a long-standing partnership in the field of criticality safety. In this collaboration, IRSN and JAEA are planning a joint experiment using the new STACY critical assembly, modified by JAEA. In order to compare the codes (MVP3, MORET6, etc.) and nuclear data (JENDL and JEFF) used by both institutes in the planning of the STACY experiment, benchmark calculations of the Apparatus B and TCA, which are critical assemblies once owned by both institutes, benchmarks from the ICSBEP handbook and the computational model of the new STACY were performed. Including the new STACY calculation model, the calculations include several different neutron moderation conditions and critical water heights. There were slight systematic differences in the calculation results, which may have originated from the processing and/or format of the nuclear data libraries. However, it was found that the calculated results, including the new codes and the new nuclear data, are in good agreement with the experimental values. Therefore, there are no issues to use them for the design of experiments for the new STACY. Furthermore, the impact of the new TSL data included in JENDL-5 on the effective multiplication factor was investigated. Experimental validation for them will be completed by critical experiments of the new STACY by both institutes.
Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nagayama, Masahiro*
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-006, 24 Pages, 2023/07
Core fuels with stainless steel cladding and high plutonium content mixed oxide (MOX) fuel in a water-cooled environment, such as supercritical water-cooled reactors (SCWR) and reduced-moderation water reactors (RMWR), have been studied. In order to contribute to the research and development of such a core fuel concept, the fuel performance code "FEMAXI-8" was verified based on the results of post irradiation examinations of MOX fuel irradiated in the experimental fast reactor "JOYO". FEMAXI-8 is the latest version of the behavior analysis code developed by JAEA to analyze the behavior of light water reactor fuels under normal operation and transient conditions. This latest code has been improved and developed to allow the selection of stainless steel cladding property models to analyze improved fuels such as accident tolerant fuels. The purpose of this report is to confirm the prediction accuracy of FEMAXI-8 for the irradiation behavior of the new type of core fuel that is currently being developed. As a result of the verification, it was confirmed that FEMAXI-8 has sufficient analysis accuracy for the irradiation behavior of sodium-cooled fast reactor MOX fuel with stainless steel cladding, which exceeds the plutonium content and irradiation conditions of light water reactors. In the future, the analysis accuracy of FEMAXI-8 could be improved by adopting the O/M ratio dependence of MOX fuel thermal conductivity and the irradiation behavior evaluation model at high temperature.
Sato, Ikken; Yoshikawa, Shinji; Yamashita, Takuya; Cibula, M.*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 404, p.112205_1 - 112205_21, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:90.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)Based on updated knowledge from plant-internal investigations, experiments and model simulations until now, the in-vessel phase of Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Unit 2 was analyzed using the MAAP code. In Unit 2, it is considered that the core material enthalpy was relatively low when it relocated to the lower plenum of the pressure vessel, then, cooled by the coolant and solidified there. Although the MAAP code tended to underestimate the degree of core-material oxidation during the relocation, this probable underestimation was compensated for by an existing study that was considered more reliable, so that more realistic debris conditions in the lower plenum could be obtained. Basic validity of the former prediction of the Unit 2 accident progression behavior was confirmed and detailed boundary condition for the later phase was provided. This boundary condition should be utilized for future studies addressing debris reheating process leading to lower head failure and debris relocation toward the pedestal.
Okumura, Keisuke; Sakamoto, Yukio*; Tsukiyama, Toshihisa*
Shahei Kaiseki No V&V Gaidorain Sakutei Ni Mukete, p.4 - 8, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Seki, Misaki; Shibata, Akira; Nakamura, Jinichi; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-018, 42 Pages, 2022/03
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) in Oarai Research and Development Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developing various reactor materials, irradiation techniques and instruments for more than 30 years. Among them, the development of self-powered neutron detectors (SPNDs) and gamma detectors (SPGDs) has been carried out, and several research results have been reported. However, most of the results are based on the design study of the detector development and the results of in-core irradiation tests and gamma irradiation tests using Cobalt-60. In this report, a numerical code is developed based on the paper "Neutron and Gamma-Ray Effects on Self-Powered In-Core Radiation Detectors" written by H.D. Warren and N.H. Shah in 1974, in order to theoretically evaluate the self-powered radiation detectors.
Okamura, Tomohiro*; Nishihara, Kenji; Katano, Ryota; Oizumi, Akito; Nakase, Masahiko*; Asano, Hidekazu*; Takeshita, Kenji*
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-016, 43 Pages, 2022/03
The quantitative prediction and analysis of the future nuclear energy utilization scenarios are required in order to establish the advanced nuclear fuel cycle. However, the nuclear fuel cycle consists of various processes from front- to back-end, and it is difficult to analyze the scenarios due to the complexity of modeling and the variety of scenarios. Japan Atomic Energy Agency and Tokyo Institute of Technology have jointly developed the NMB code as a tool for integrated analysis of mass balance from natural uranium needs to radionuclide migration of geological disposal. This user manual describes how to create a database and scenario input for the NMB version 4.0.
Malins, A.; Lemoine, T.*
Journal of Open Source Software (Internet), 7(71), p.3318_1 - 3318_6, 2022/03
Okamura, Tomohiro*; Oizumi, Akito; Nishihara, Kenji; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takeshita, Kenji*
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-023, 32 Pages, 2021/03
Nuclear Material Balance code (NMB code) have been developed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The NMB code will be updated with the function of mass balance analysis at the backend process such as reprocessing, vitrification and geological disposal. In order to perform its analysis with high accuracy, it is necessary to expand the number of FP nuclides calculated in the NMB code. In this study, depletion calculation by ORIGEN code was performed under 3 different burn-up conditions such as spent uranium fuel from light water reactor, and nuclides were selected from 5 evaluation indexes such as mass and heat generation. In addition, the FP nuclides required to configure a simple burnup chain with the same calculation accuracy as ORIGEN in the NMB code was selected. As the result, two lists with different number of nuclides, such as "Detailed list" and a "Simplified list", were created.
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.03014_1 - 03014_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:86.93(Nuclear Science & Technology)Intensive neutron sources using deuteron accelerators have been proposed for various applications such as irradiation test for fusion reactor materials and production of radioisotopes for medical use. In addition, transmutation system using deuteron-induced spallation reactions has been recently proposed for LLFPs. Accurate and comprehensive deuteron nuclear data are indispensable in the design study of such facilities. Under the above situations, we have been developing a code system dedicated for deuteron-induced reactions, which is called DEURACS. In the present work, calculations using DEURACS are compared with available experimental data up to 200 MeV such as DDXs for emission of neutron or light charged particles. We also analyze isotopic production cross sections of residual nuclei. Validation of the present modelling in DEURACS is discussed through comparison with the experimental data.
Yoshikawa, Shinji
JAEA-Technology 2019-024, 22 Pages, 2020/03
In various technical fields of nuclear energy, computer codes are often used for transient simulations of target phenomena. Some of the codes were developed many years ago and have been revised with newly acquired findings, rather than newly developed, because of many encompassed numerical models and complexity of algorithms. In many cases, available outputs for users are output text files and graphs showing temporal variations of parameters, despite diversified and huge number of output information items are posing difficulty to the users in grasping the whole picture of the reproduced phenomena. This report compiles a series of know-hows in building a post-processor software for large simulation codes which serves as an interactive tool for code users in understanding the reproduced consequence with visually understandable information items. These know-hows are acquired through post-processor developments for LWR severe accident simulation codes RELAP/SCDAPSIM and MELCOR.
 C
CLiu, X.*; Morita, Koji*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.47 - 51, 2019/09
Investigation of the eutectic reaction in a core disruptive accident of sodium cooled reactor is of importance since reactor criticality will be affected by the change in reactivity after eutectic reaction. In this study, we performed 1st step of validation analysis using a fast reactor safety analysis code, SIMMER-III, with the developed model based on a new series of experiments, where a B C pellet was immersed into a molten stainless steel (SS) pool. The simulation results showed the general behavior of eutectic material formation measured in the experiments reasonably. The eutectic reaction consumes solid B
C pellet was immersed into a molten stainless steel (SS) pool. The simulation results showed the general behavior of eutectic material formation measured in the experiments reasonably. The eutectic reaction consumes solid B C and liquid SS, and then the liquid eutectic composition is produced at the early stage of reaction due to the high temperature of molten SS. Movement of the eutectic material in the molten pool leads to the redistribution of boron element. Molten SS pool then freezes to solid SS and movement of eutectic material is stopped by surrounding solid SS. Boron concentration in the pool was measured after molten SS freezes into a solid. Simulation results indicate that boron tends to accumulate in the upper part of the molten pool. This is attributed to the buoyancy force acting on lighter boron in the molten SS pool. A parametric study was also conducted by changing the initial temperature of B
C and liquid SS, and then the liquid eutectic composition is produced at the early stage of reaction due to the high temperature of molten SS. Movement of the eutectic material in the molten pool leads to the redistribution of boron element. Molten SS pool then freezes to solid SS and movement of eutectic material is stopped by surrounding solid SS. Boron concentration in the pool was measured after molten SS freezes into a solid. Simulation results indicate that boron tends to accumulate in the upper part of the molten pool. This is attributed to the buoyancy force acting on lighter boron in the molten SS pool. A parametric study was also conducted by changing the initial temperature of B C pellet and SS to investigate the temperature sensitivity on the eutectic reaction behavior.
C pellet and SS to investigate the temperature sensitivity on the eutectic reaction behavior.
Fukano, Yoshitaka
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 5(1), p.011001_1 - 011001_13, 2019/01
Local subassembly faults (LFs) have been considered to be of greater importance in safety evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs) because fuel elements were generally densely arranged in the subassemblies (SAs) in this type of reactors, and because power densities were higher compared with those in light water reactors. A hypothetical total instantaneous flow blockage at the coolant inlet of an SA (HTIB) gives most severe consequences among a variety of LFs. Although an evaluation on the consequences of HTIB using SAS4A code was performed in the past study, SAS4A code was further developed by implementing analytical model of power control system in this study. An evaluation on the consequences of HTIB in an SFR by this developed SAS4A code clarified that the conclusion in the past study was almost same as that in this study. Furthermore SAS4A code was newly validated using four in-pile experiments which simulated HTIB events. The validity of SAS4A application to safety evaluation on the consequence of HTIB was further enhanced in this study. Thus the methodology of HTIB evaluation was established in this study together with the past study and is applicable to HTIB evaluations in other SFRs.
 -ray exposure buildup factors
-ray exposure buildup factorsMatsuda, Norihiro; Onishi, Seiki*; Sakamoto, Yukio*; Nobuhara, Fumiyoshi*
Heisei 29-Nendo Kani Shahei Kaiseki Kodo Rebyu Wakingu Gurupu Katsudo Hokokusho (Internet), p.20 - 28, 2018/08
no abstracts in English
Suyama, Kenya; Yokoyama, Kenji
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (119), p.38 - 47, 2018/02
We have developed numerous neutronics calculation codes in Japan. However, development of the one-point burnup calculation code which replaces the still widely used ORIGEN2 code has not been successful. The one point burnup code is indispensable to evaluate the characteristics of the used nuclear fuel increasing in Japan, and it uses all evaluated nuclear data including the fission yield and decay data as well as cross section data. It means that it could be the Killer Application in the field of the nuclear data and neutronics code. This report describes the necessity of the one point burnup calculation code development in Japan and required function and performance which have been considered by authors.
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Kono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ye, T.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.12025_1 - 12025_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:90.81(Nuclear Science & Technology)Recently, intensive neutron sources using deuteron accelerator have been proposed for various applications. Accurate and comprehensive deuteron nuclear data library over wide ranges of target mass number and incident energy are indispensable for the design of deuteron accelerator neutron sources. Thus, we have developed an integrated code system dedicated for analysis and prediction of deuteron-induced reactions, which is called DEUteron-induced Reaction Analysis Code System (DEURACS). In the present work, the analysis of  reactions is extended to higher incident energy up to nearly 100 MeV and also DEURACS is applied to
reactions is extended to higher incident energy up to nearly 100 MeV and also DEURACS is applied to 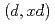 reactions at 80 and 100 MeV. The DEURACS calculations reproduce the experimental double-differential cross sections for the
reactions at 80 and 100 MeV. The DEURACS calculations reproduce the experimental double-differential cross sections for the  and
and 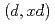 reactions well.
reactions well.
Fukano, Yoshitaka
Proceedings of 25th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-25) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/07
An evaluation on the consequences of a hypothetical total instantaneous flow blockage at the coolant inlet of an SA (HTIB) using SAS4A code was also performed in the past study. SAS4A code was further developed by implementing analytical model of power control system in this study. An evaluation on the consequences of HTIB in Monju by this developed SAS4A code was performed. It was clarified by the analyses considering power control system that the reactor would be safely shut down by the plant protection system triggered by either of 116 percent over power or delayed neutron detector trip signals. Therefore the conclusion in the past study that the consequences of HTIB event would be much less severe than that of unprotected loss-of-flow event was strongly supported by this study. Furthermore SAS4A code was newly validated using an in-pile experiment which simulated HTIB events. The validity of SAS4A application to safety evaluation on the consequence of HTIB was further enhanced in this study.